Heather Peluso, DO1, Wesley B Jones, MD1, Marwan S Abougergi, MD2. 1Greenville Health System, 2Catalyst Medical Consulting, LLC
Introduction: Antibiotics are frequently used to treat acute pancreatitis before the presence of infected necrosis is established, which predisposes patients to Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI). We sought to determine the impact of CDI on mortality, 30-day readmission, morbidity and resource utilization among patients with acute pancreatitis in the United States.
Methods: Retrospective cohort study using the 2014 National Readmission Database, the largest publicly available national readmission database. Patients were included if they had a principal diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Exclusion criteria were age <18 years and December admission. Readmission was defined as the first admission to any hospital for any non-trauma diagnosis within 30 days of the index admission. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality rate. Secondary outcomes were 30-day readmission, morbidity (intensive care unit (ICU) admission, systemic inflammatory response syndrome with organ failure (SIRS/OF), total parenteral nutrition (TPN), shock) and resource utilization (length of stay (LOS), total hospitalization costs and charges). The following confounders were accounted for using multivariate regression analysis: age, sex, median income in patient’s zipcode, Charlson comorbidity score, hospital urban location, bedsize, teaching status.
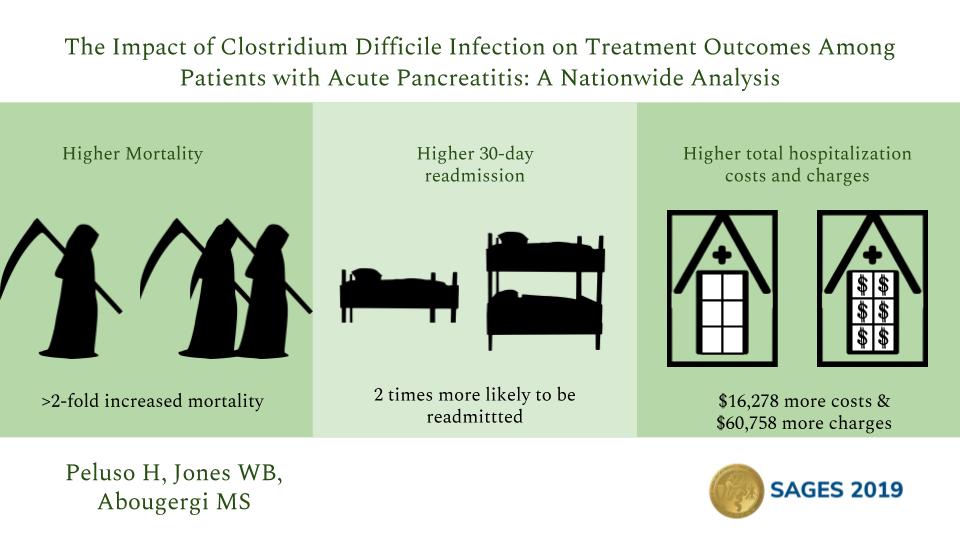
Results: 236,066 patients were included, 2,362 of whom developed CDI. The mean age was 52.3 years and 47% were female. After adjusting for confounders, CDI was associated with >2-fold increase in mortality (adjusted odds ratio (aOR: 2.64 (1.70-4.12),p<0.01). In addition, patients with CDI were twice as likely to be readmitted within 30 days ( aOR: 1.97 (1.68-2.30),p<0.01). CDI was associated with a substantial increase in morbidity: ICU admission (aOR: 9.07 (6.88-11.96), p<0.01), SIRS/OF (aOR: 3.26 (1.72-6.17),p<0.01), TPN (aOR: 5.68 (4.55-7.08),p<0.01), and shock (aOR: 6.50 (4.51-9.36),p<0.01). Finally, CDI was associated with significantly higher resource utilization: LOS (adjusted mean difference (aMD): 7.07 (6.33-7.81) days,p<0.01), total hospitalization costs (aMD: $16,278 ($13,820-$18,736),p<0.01) and charges (aMD: $60,758 ($49,896-$71,620),p<0.01).
Discussion: The development of CDI among patients with acute pancreatitis has a detrimental effect on treatment outcomes. It is associated with substantially higher mortality, 30-day readmission, morbidity and resource utilization. Therefore, judicious antibiotics use in this setting is of crucial importance and should be advocated for at the national level.
Presented at the SAGES 2017 Annual Meeting in Houston, TX.
Abstract ID: 94219
Program Number: P235
Presentation Session: Poster Session (Non CME)
Presentation Type: Poster