Rk Singh, MCh, J Abraham, MS, Hm Lokesh, MCh, A Prakash, MS, A Behari, MS, Ak Gupta, MCh, Vk Kapoor, MS, R Saxena, MS. Dept. of Surgical Gastroenterology & Liver Transplant, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
INTRODUCTION: Splenectomy for hematologic diseases is now performed mostly laparoscopically. Laparoscopic splenectomy is an advanced surgical procedure with a definite learning curve. We present our initial experience of laparoscopic splenectomy for hematologic diseases with analysis of factors predicting conversion and postoperative morbidity.
METHODS: Forty-one consecutive patients underwent laparoscopic splenectomy for hematological diseases (Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura – 33, Hereditary spherocytosis – 2,Thalassemia -2, Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia -2, Miscellaneous- 2) at a single centre. Retrospective analysis was carried out for factors predictive of conversion to open splenectomy and postoperative morbidity. Statistical analysis was done with SPSS software and tests used were chi-square, t-test and Mann-Whitney test.
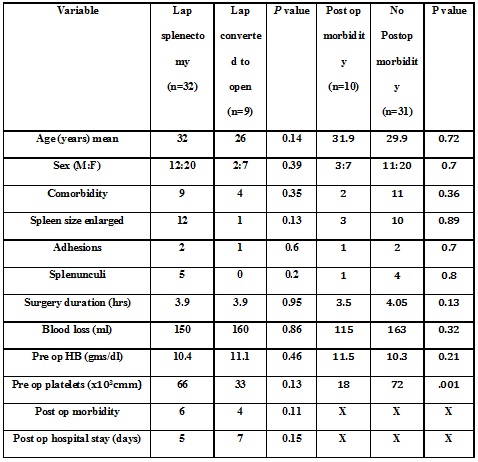
RESULTS: Mean age (SD) was 30.4yrs (14.7) and gender ratio was M:F= 14:27. The mean operation time (SD) was 3.9hrs (0.9). Conversion to open splenectomy was done in 9 patients (24%). The reason for conversion was intraoperative bleeding in 50% patients. The postoperative overall morbidity and mortality were 21.9% and 4.8% respectively. The age, gender, preoperative comorbidity, spleen size, intraabdominal adhesions, presence of splenenculi, duration of surgery, blood loss, preoperative and postoperative hemoglobin and platelet count, postoperative morbidity & postoperative stay were analyzed to assess the impact on conversion. None of the analyzed factors was found to correlate with conversion to open splenectomy. Postoperative morbidity predominantly consisted of postoperative fever & persisting low platelet count. Preoperative platelet count was the only factor that was predictive of postoperative morbidity (p=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS: Laparoscopic splenectomy has a high conversion rate in the initial experience. However, with a low threshold of conversion laparoscopic splenectomy can be carried out safely with acceptable morbidity and mortality.
Session Number: Poster – Poster Presentations
Program Number: P600
View Poster