Wen Hui Tan, MD, Jared McAllister, MD, Sara Feaman, MA, CCRP, Jeffrey A Blatnik, MD. Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine
Introduction: In recent years, a number of surgeons have moved to performing ventral or incisional hernia repairs robotically, touting advantages such as better ergonomics and more degrees of freedom. One persistent critique of utilizing a robotic approach is the cost, much of which come from operating room and supply costs; however, there may not be a correlation between cost and improved outcomes. If a preperitoneal technique is performed robotically, it may be possible to offset the cost of a barrier coated mesh and disposable fixation devices. The objective of this study was to compare disposable operating room costs and technical direct costs of the first 90 days postoperatively between patients undergoing robotic and laparoscopic ventral hernia repair. Our hypothesis was that a robotic approach provides similar short-term clinical outcomes at similar cost when compared to performing ventral hernia repairs laparoscopically.
Methods: A retrospective review of patients who underwent robotic or laparoscopic ventral hernia repairs by a single surgeon at an academic center was performed. The primary outcome was disposable operating room costs. Secondary outcomes included technical direct costs such as costs from the laboratory or pharmacy, and clinical outcomes including operative time and length of stay. The Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test was used to compare costs, age, and BMI between groups, and Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test was used to compare categorical data.
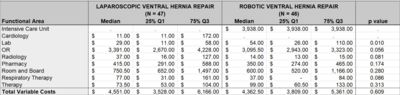
Results: There were 93 patients included in this study: 47 laparoscopic and 46 robotic ventral hernia repairs. Gender and BMI were similar for the two groups; however, the mean age in the robotic group was significantly younger (55.1 vs. 61.6 years, p=0.02). There was no statistically significant difference in wound class or number of patients undergoing a repair for a recurrent hernia, but the hernia size in the robotic group was significantly larger (44.5 vs. 24 cm2, p=0.0012). Comparing clinical outcomes, the laparoscopic approach was associated with a significantly increased operative time, but there was no significant difference in length of stay or surgical site occurrences. Total variable costs were similar between groups (median $4,551.00 vs. $4,362.50, p=0.609), and ranged from $3,528-$6,166. For the majority of patients, the bulk of costs came from three functional areas: the operating room, room and board, and pharmacy. These were not statistically significantly different between groups.
Conclusion: Performing ventral hernia repairs robotically in a preperitoneal fashion may provide similar short-term clinical outcomes at similar cost when compared to performing ventral hernia repairs laparoscopically.
Presented at the SAGES 2017 Annual Meeting in Houston, TX.
Abstract ID: 87015
Program Number: S052
Presentation Session: Robotics 1 Session
Presentation Type: Podium